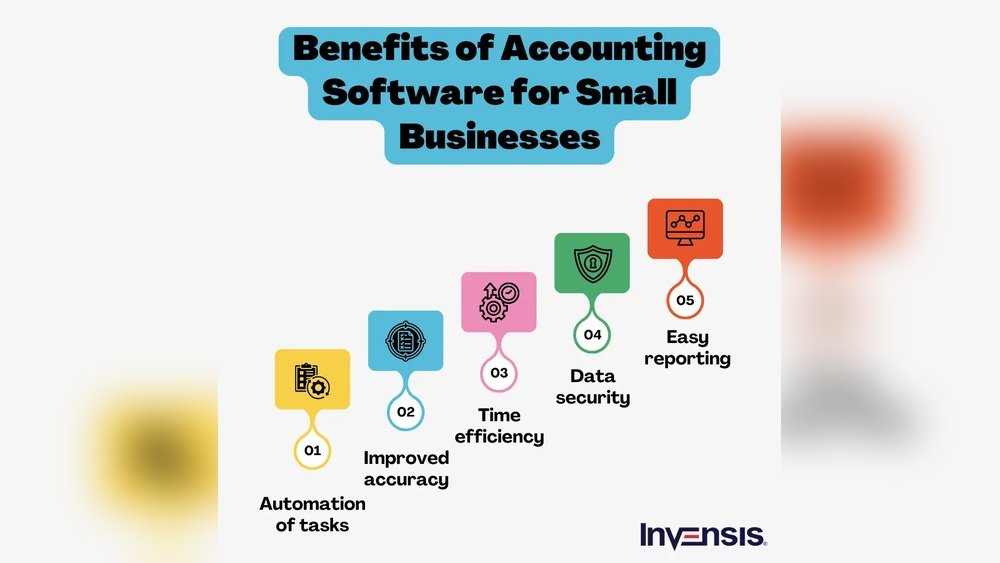
Are you tired of juggling endless spreadsheets and confusing numbers for your small business? Imagine having accounting software tailored just for your needs—simple, reliable, and made to save you time and stress.
Creating your own accounting software might sound complicated, but it doesn’t have to be. You’ll discover clear, step-by-step guidance on how to build software that works perfectly for your business. Ready to take control of your finances like never before?
Keep reading, and let’s make it happen together.
Planning Your Software
Start by choosing key features that small businesses need. These include expense tracking, invoicing, and basic reporting. Keep the design simple and easy to use. Understanding your target audience is crucial. Know their business size, industry, and tech comfort. This helps create software they will like and use.
Set clear project goals. Decide what problems your software will solve. Plan how to measure success. Goals can include saving time or reducing errors. Keep the list short and focused. This helps keep the project on track.
Credit: financfy.com
Choosing The Technology Stack
Frontend options include React, Angular, and Vue.js. These help build user-friendly interfaces. React is popular for its simplicity. Angular offers a full-featured framework. Vue.js is easy to learn and flexible. Choose one based on your team’s skills and project needs.
Backend frameworks handle server logic and data processing. Common choices are Node.js, Django, and Ruby on Rails. Node.js is fast and uses JavaScript. Django is secure and built with Python. Ruby on Rails is good for quick development. Pick a framework that matches your app’s complexity and your developers’ experience.
Database selection is crucial for storing business data. Options include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. MySQL and PostgreSQL are great for structured data. MongoDB works well with flexible, unstructured data. Consider the type of data your software will manage before choosing.
Designing User Interface
Wireframes help show how the software will look and work. They make the design clear before coding starts. Simple shapes and lines stand for buttons and menus. This helps focus on layout and user flow.
User experience means making software easy and fun to use. Clear labels and big buttons help people find things fast. Avoid clutter to keep screens neat. Test with real users to fix problems early.
| Aspect | Mobile Design | Desktop Design |
|---|---|---|
| Screen Size | Small, touch screen | Large, mouse and keyboard |
| Navigation | Simple, easy taps | More options visible |
| Performance | Fast loading, less data | Can handle more features |
| Layout | Vertical, single column | Multi-column, detailed |
Developing Core Modules
Transaction Management lets users record all money movements. It keeps track of sales, purchases, and payments. Accurate records help avoid errors and save time. Users can view transactions by date or type. This module supports easy editing and deleting of entries.
Invoice and Billing creates and sends bills to customers quickly. It includes templates to fill in details like items, prices, and taxes. Automated billing saves effort. Users can set payment due dates and track unpaid invoices. Reminders help ensure on-time payments.
Expense Tracking records all business costs. This helps control spending and plan budgets. Users can add expenses by category, such as rent, supplies, or utilities. Reports show where money goes each month. Keeping expenses organized aids in tax filing.
Financial Reporting summarizes income and expenses. Reports include profit and loss, cash flow, and balance sheets. These reports help understand business health. Visual charts make data easy to read. Regular reports support smart decisions and planning.
Implementing Security Measures
Data encryption keeps business information safe by turning it into secret code. This code can only be read with a special key. It stops others from seeing private data.
User authentication checks who is trying to use the software. It asks for a username and password. This step helps block unauthorized users from entering.
Regular backup and recovery saves copies of all important data. If data is lost or damaged, these copies help bring it back quickly. This protects the business from data loss disasters.
Testing And Debugging
Unit Testing checks small parts of the software. Each function gets tested alone. This helps find bugs early. It saves time and effort later.
Integration Testing looks at how parts work together. It finds problems between connected parts. This ensures smooth data flow and operation.
User Acceptance Testing lets real users try the software. They check if it meets their needs. Feedback helps fix issues before launch.
Deployment And Maintenance
Setting up hosting means choosing a safe place to store your software online. Pick a host with good speed and security. This helps your software work fast and keeps data safe. Cloud hosting is popular for small business software. It lets you scale up if many users join.
Ongoing support is key to keep the software running well. Offer easy ways for users to ask questions or report problems. Quick answers build trust and help users feel confident. Regular checks can catch issues before they grow.
Regular updates keep the software fresh and bug-free. Updates add new features and fix security holes. Schedule updates during low-use times to avoid disruption. Always test updates well before release to avoid new problems.

Credit: www.pcmag.com
Marketing And User Training
Promoting your software is key to reaching small business owners. Use social media, email campaigns, and local ads to spread the word. Show how your software helps save time and money.
Creating easy-to-follow tutorials helps users learn fast. Use videos, step-by-step guides, and FAQs. Clear tutorials reduce confusion and support requests.
Gathering user feedback improves your software. Ask users what works and what doesn’t. Use surveys, reviews, and direct conversations. Fix issues quickly to keep users happy and loyal.

Credit: financfy.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Essential Features Of Small Business Accounting Software?
Small business accounting software should include invoicing, expense tracking, bank reconciliation, and financial reporting. It must be user-friendly and support tax calculations to simplify bookkeeping and compliance.
How Much Does It Cost To Develop Accounting Software?
Development costs vary by features, complexity, and platform. Basic software can start from a few thousand dollars, while advanced solutions may cost tens of thousands or more.
Which Programming Languages Are Best For Accounting Software?
Popular languages include Python, Java, C, and JavaScript. These offer robust libraries and frameworks for financial calculations and data security.
How To Ensure Data Security In Accounting Software?
Implement encryption, secure user authentication, and regular data backups. Use secure coding practices to protect sensitive financial information from breaches.
Conclusion
Building accounting software for small business takes clear steps and focus. Start with simple features that handle basic tasks well. Test your software often to fix bugs and improve use. Keep the design clean and easy to understand. Remember, your goal is to help small business owners save time and avoid errors.
With patience and practice, you can create a tool that supports their success. Keep learning and adjusting your software to meet real needs. Small efforts lead to useful results.